Do you know the difference between absolute pressure and gauge pressure? What do positive and negative pressures mean? Where is the application for the compound pressure gauge? SJ Gauge let you just by reading this article, you can have a deeper understanding of the measurement standard for different types of pressure gauges.
1. What Is Pressure?
"Pressure" is the measure of force acting perpendicular to a unit area, common units are Kg/cm2, Bar, Psi.
2. Atmospheric Pressure:
The air pressure measured at sea level is approximately 1 kg/cm2, which is the weight of the air in the atmosphere, so it is also known as atmospheric pressure with atm as the unit. 1 kg/cm2 is approximate to 1 atm. The actual value of atmospheric pressure will vary with elevation, temperature, weather, etc.
3. Absolute Pressure and Gauge Pressure:
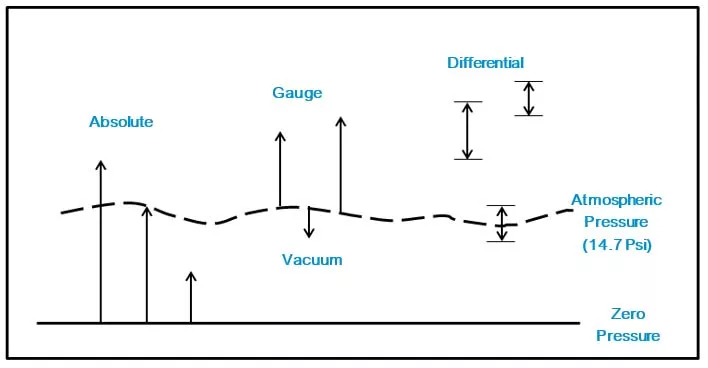
Absolute pressure:
It occurs when the gauge is completely absent. There is no negative value in absolute pressure, absolute pressure has the same benchmark and will not fluctuate when measuring.
Absolute pressure can be regarded as the gauge pressure plus the atmospheric pressure. That is to say, the difference between the absolute pressure and the gauge pressure is whether the atmospheric pressure is included when measuring. When you need a measurement that is not impacted by atmospheric pressure, you can use the absolute pressure gauge, for example: the food industry uses absolute pressure gauge while packaging to ensure the freshness of food.
 |
 |
|
Figures 1 |
Figures 2 |
Figures 1 and 2 show the pressure values of the absolute pressure gauge at 1 atm (approximate to 100 kPa)
Gauge pressure:
For barometric pressure, measured based on atmospheric pressure, the measurement benchmark is not fixed. It may change with the environment, and the measurement result can be negative.
The gauge pressure is measured by atmospheric pressure as the benchmark, so different environments may have different measurement reference points, for example: the atmospheric pressure is relatively low on rainy days in the same place. The measurement value can be negative due to the difference between pressure sources. This is common for vacuum pressure gauges and compound pressure gauges. The pressure value displayed on the dial does not represent the real pressure of the medium.
Gauge pressure (Pg) = Absolute pressure (Pabs) - Atmospheric pressure (atm)
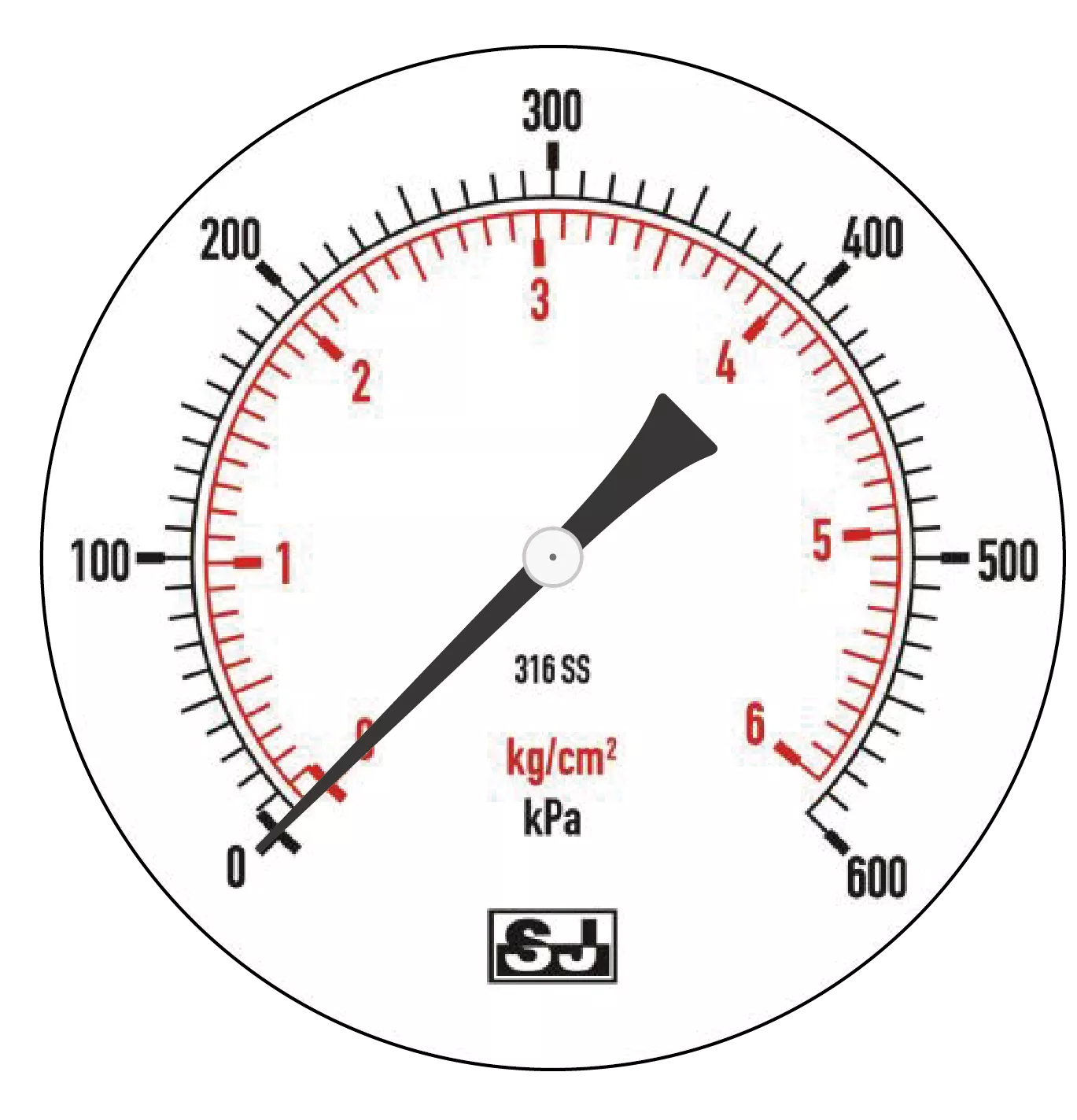

Figure 3
Figure 3 shows the pressure value of a positive gauge at 1 atm (approximate to 100 kPa)
4. Vacuum/Negative Pressure:
When the medium pressure is lower than the atmospheric pressure, it creates a vacuum — which is also known as negative pressure. Both vacuum pressure gauges and compound pressure gauges can be used to measure negative pressure, which is mostly used in the food industry.
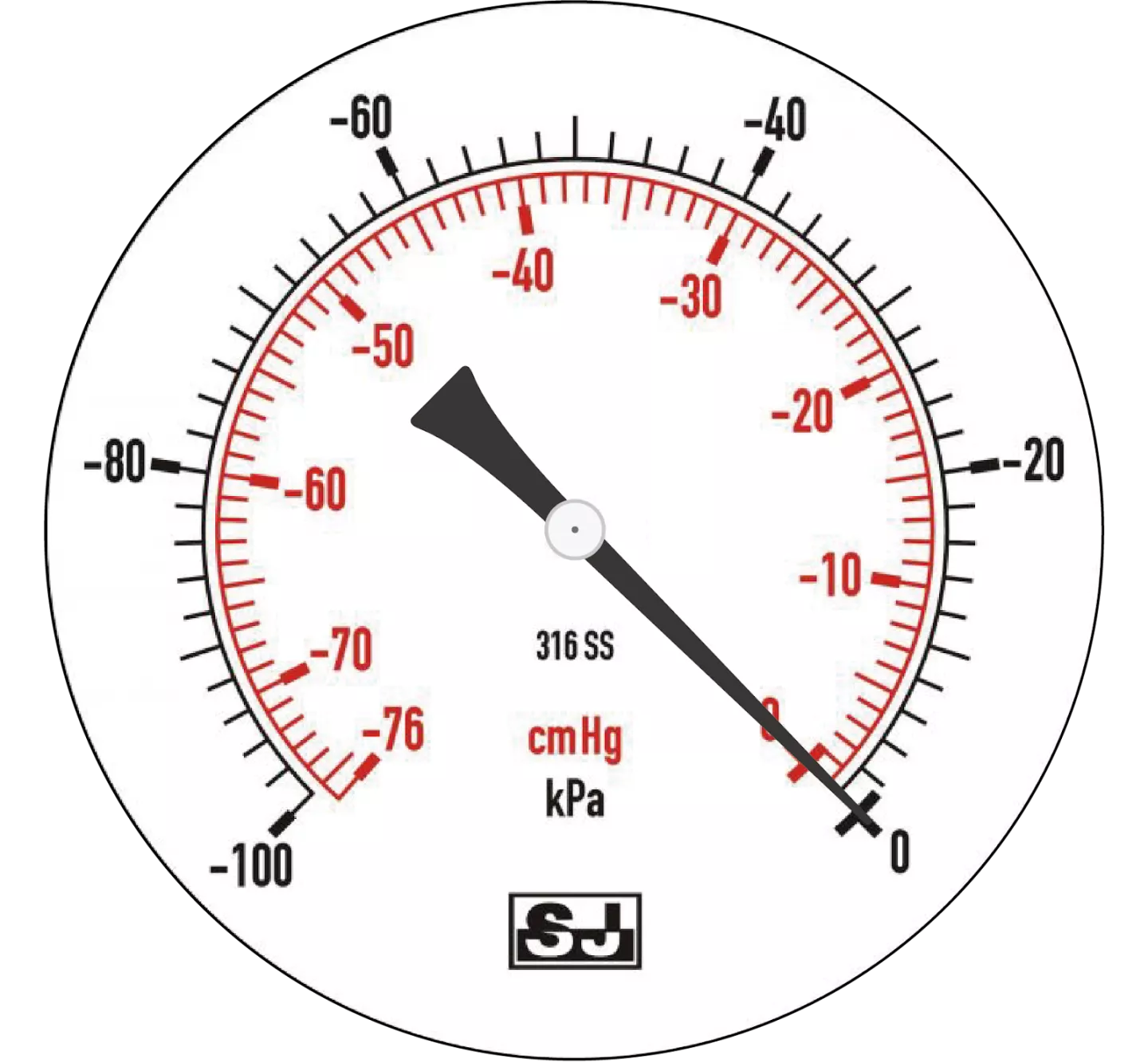

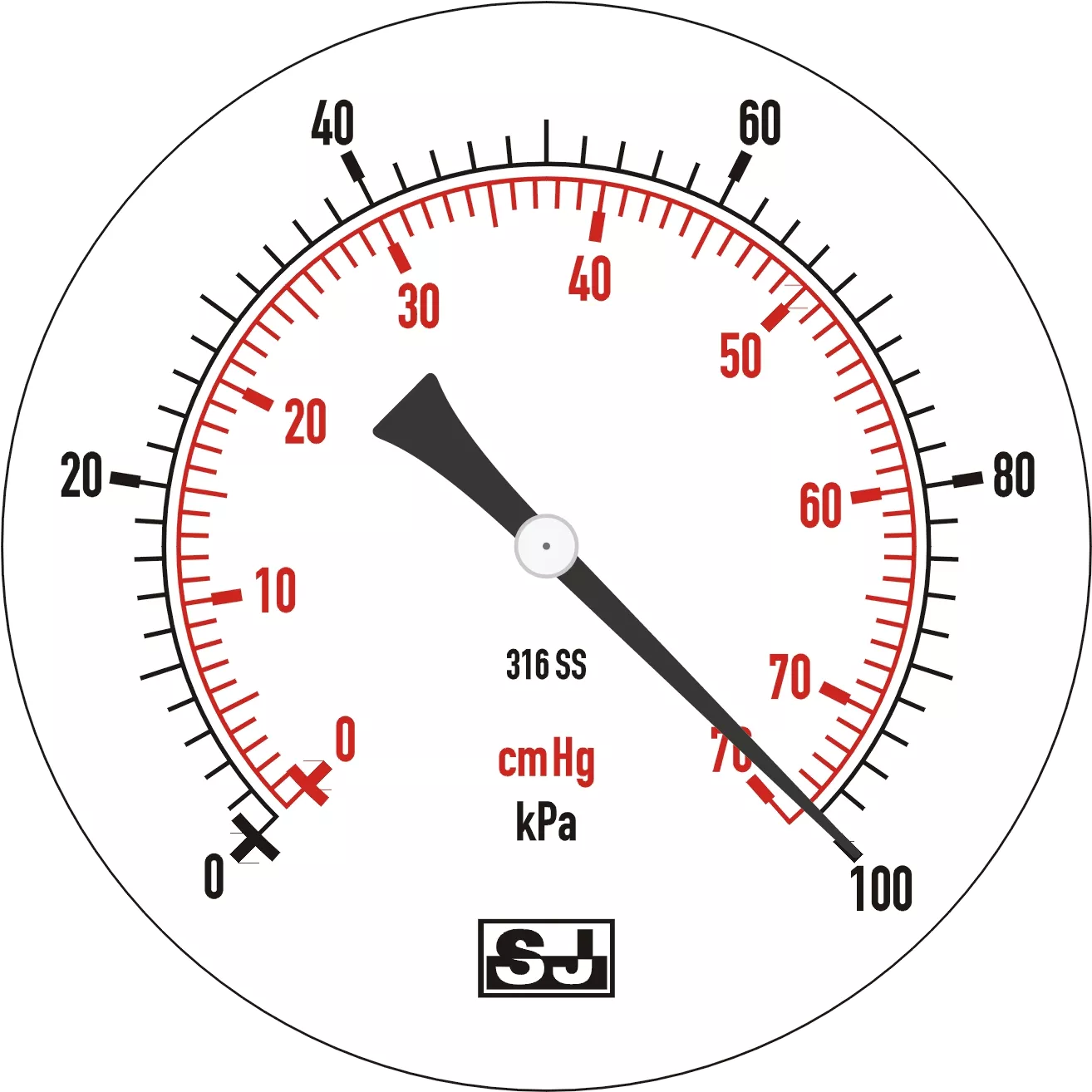
Figure 4
Figure 4 shows the pressure value of the negative pressure gauge at 1 atm
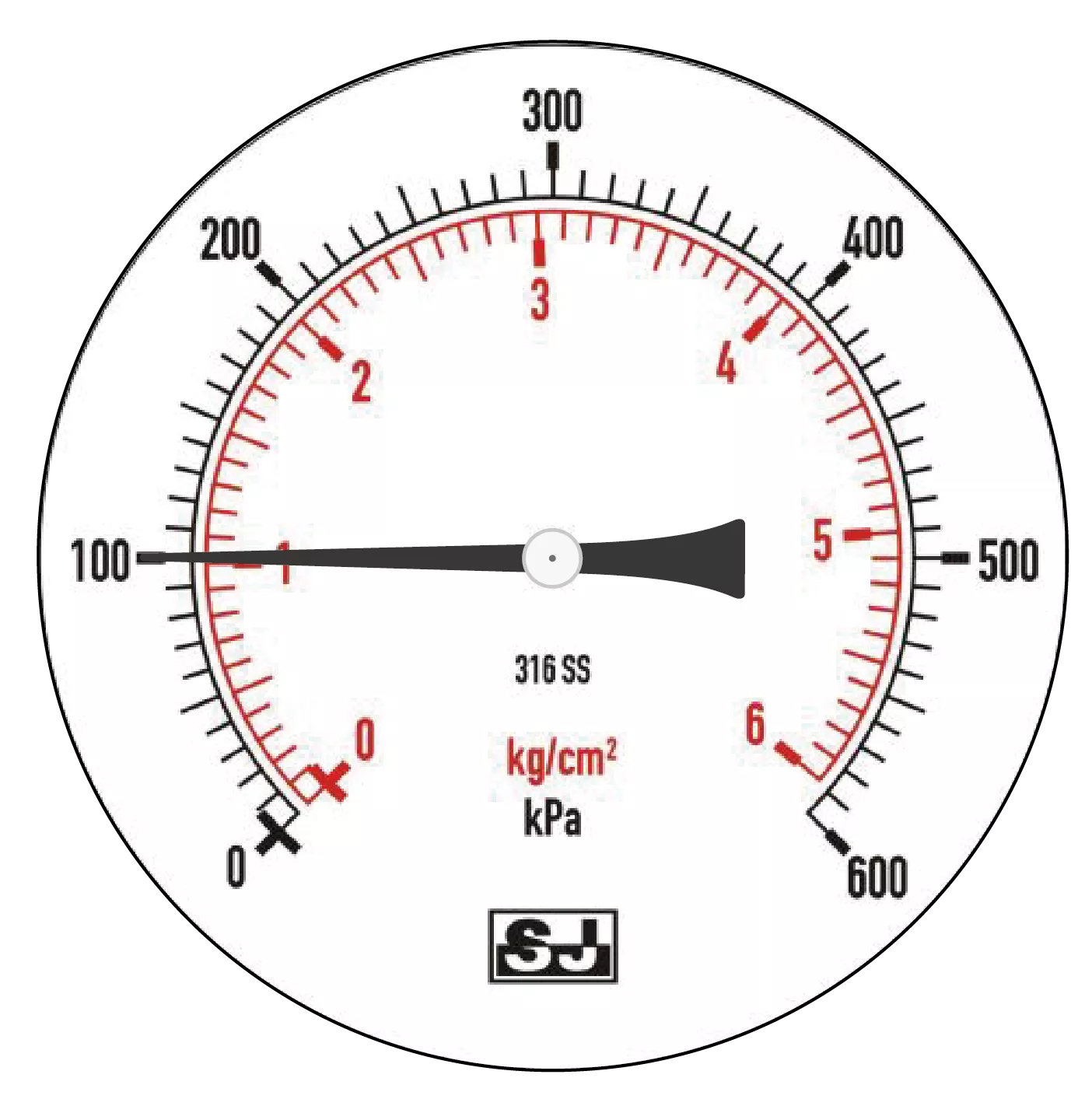
5. Compound Pressure:
Compound pressure measures both positive and negative pressure at the same time, when measuring positive pressure, the pointer will move clockwise, and it will move counterclockwise when measuring negative pressure. Compound pressure gauges are commonly used in pump measurement, HVAC systems and fire control instruments.

Figure 5
Figure 5 shows the pressure value of the compound pressure gauge at 1 atm
We hope you now have a basic understanding when it comes to the measurement standard for different types of pressure gauges. Do you want to know about specifications to consider when purchasing general pointer pressure gauges? Or how to solve pressure gauge failure? Click the links below to learn more!








