Are you feeling overwhelmed by terms like "thread," "process connection," "connector," and "fitting"?
Not to mention the various regional common standards and specifications to contend with.
Interested in finding the best fit for your specific application requirements?
Explore the four primary thread connection types SJ Gauge offers: NPT, PT, G and M.
We will introduce each of these frequently used thread connection types and identify the distinctions between them.
You can also contact our professional sales team, and we will do our best to provide you with the most suitable customized measurement solutions for your application.
Contents
- 01What Are Threads? What Are Their Functions?
- 02What Problems Can Arise from Choosing the Wrong Thread Connection Type?
- 03Two Measuring Tools to Know Before Selecting Threads(a) Vernier Caliper
(b) Thread Gauge - 04Identifying Threads in Four Simple Steps
- (a) Determine If the Thread Is Straight (Parallel) or Tapered (Conical)
(b) Determine the Type of Thread and Pitch
(c) Determine the Size of the Connector
(d) Refer to Various Thread Standard Tables (Straight, Taper, Size, Pitch, Size) - 05Four Steps to Identify Thread Specifications
02. What Problems Can Arise from Choosing the Wrong Thread Connection Type?
03. Two Measuring Tools to Know Before Selecting Threads
(a) Vernier Caliper
(b) Thread Gauge
04. Identifying Threads in Four Simple Steps
(a) Determine If the Thread Is Straight (Parallel) or Tapered (Conical):
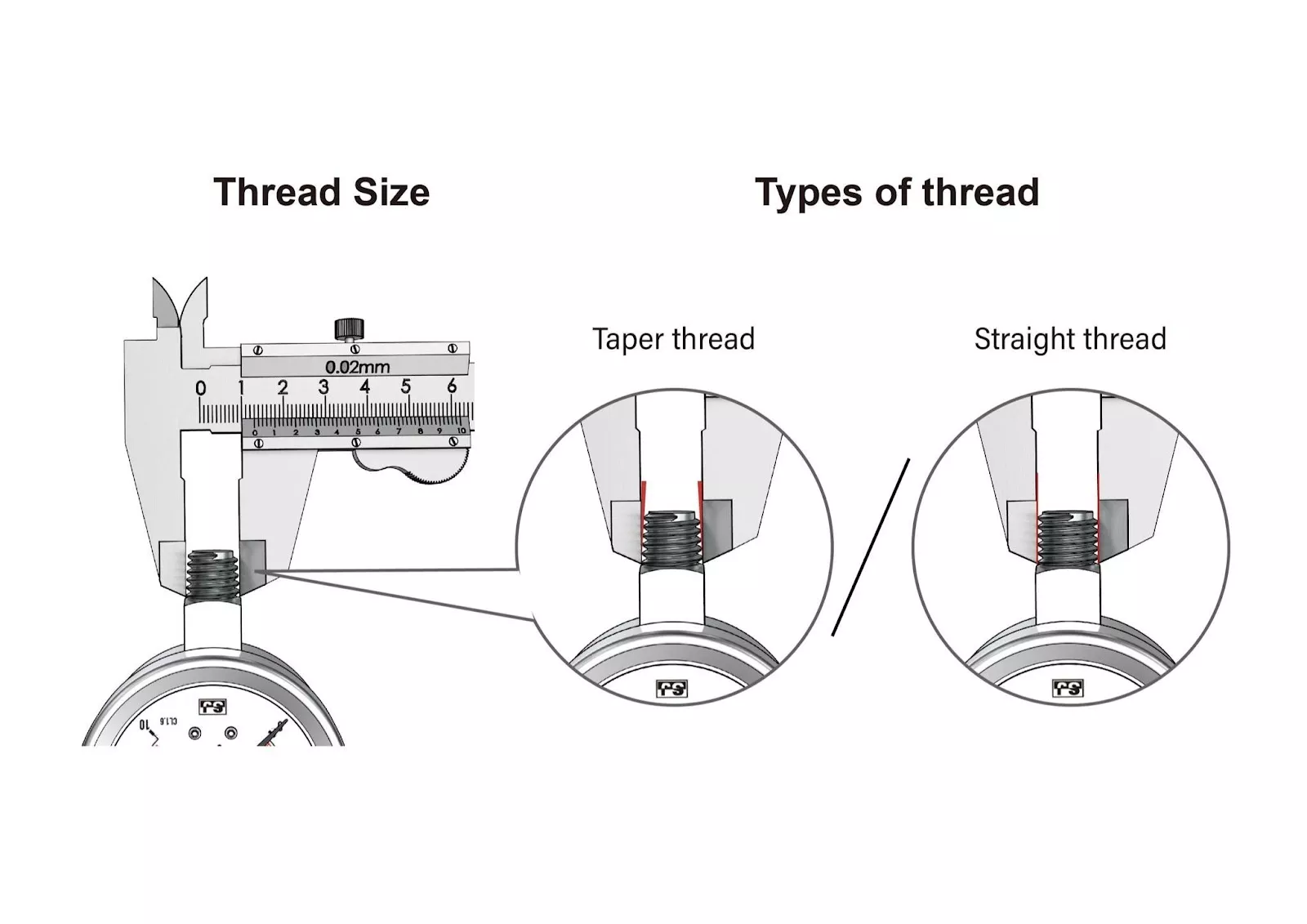
(b) Determine the Type of Thread and Pitch
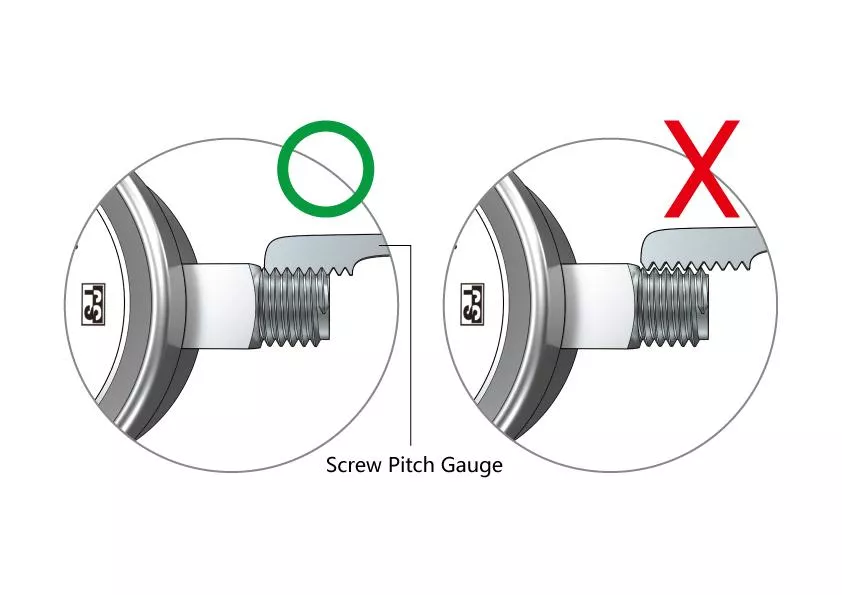
(c) Determine the Size of the Connector
(d) Refer to Various Thread Standard Tables (Straight, Taper, Size, Pitch, Size)
You can refer to the information and tables we have compiled below, which compare the most common thread forms, including American Standard, British Standard, and Metric.
American Standard Straight Threads (SAE=UN=UNF)
The most common straight thread form in the United States is UN/UNF (Unified National Fine) threads, also known as SAE (Society of Automotive Engineers)straight threads. The table below lists some common sizes for SAE straight threads.
The naming convention for American Standard straight threads is as follows: Size - Number of Threads per Inch, Type, for example, 3/4-16, UN/UNF.
|
American Standard Straight Threads SAE=UN=UNF |
|||||
|
Size |
Threads per inch (TPI) |
Thread diameter |
Thread |
||
|
(inch) |
Major |
Simple |
Minor |
||
|
5/16 |
24 |
7.938 |
7.249 |
6.792 |
60° |
|
7/16 |
20 |
11.113 |
10.287 |
9.738 |
|
|
1/2 |
20 |
12.7 |
11.875 |
11.325 |
|
|
9/16 |
18 |
14.288 |
13.325 |
12.559 |
|
|
3/4 |
16 |
19.05 |
18.019 |
17.331 |
|
|
1-1/16 |
12 |
26.988 |
25.613 |
24.695 |
|
|
1-5/16 |
12 |
33.338 |
31.963 |
31.046 |
|
|
Size-TPI, Type |
|||||
American Standard Tapered Threads (NPT / NPTF):
NPT (National Pipe Taper) American Standard Tapered Threads, officially known as American National Standard Taper Pipe Thread, are widely used in the United States for pipe connections.
NPTF American Standard Tapered Threads - Dryseal, also known as the American Standard Pipe Thread Tapered - Dryseal), are not recommended by the National Fluid Power Association (N.F.P.A.), but they are still widely utilized.
The primary difference between NPT threads and NPTF threads is that the NPT does not have a sharp crest, resulting in a small leak point after assembly, requiring the use of sealant for proper sealing.
The naming convention for American Standard Tapered Threads is as follows: Size - Number of Threads per Inch, Type, for example, 1/4-18, NPT.
|
American Standard Tapered Threads NPT / NPTF |
|||||
|
Size |
Threads per inch (TPI) |
Thread diameter |
Thread angle |
||
|
(inch) |
Major diameter |
Simple pitch diameter |
Minor diameter |
||
|
1/16 |
27 |
7.894 |
7.142 |
6.398 |
60° |
|
1/8 |
27 |
10.242 |
9.489 |
8.737 |
|
|
1/4 |
18 |
13.616 |
12.487 |
11.358 |
|
|
3/8 |
18 |
17.055 |
15.926 |
14.797 |
|
|
1/2 |
14 |
21.224 |
19.772 |
18.321 |
|
|
3/4 |
14 |
26.569 |
25.117 |
23.666 |
|
|
1 |
11.5 |
33.228 |
31.461 |
29.694 |
|
|
1-1/4 |
11.5 |
41.985 |
40.218 |
38.454 |
|
|
1-1/2 |
11.5 |
48.054 |
46.287 |
44.52 |
|
|
2 |
11.5 |
60.092 |
58.325 |
56.558 |
|
|
Size-TPI, Type |
|||||
British Standard Parallel Threads (BSPP=BSP=PF=G):
These threads adhere to standards set by the British Standards Institution (BSI). British Standard Parallel Threads are commonly referred to using one of four terms: G Thread, BSPP (British Standard Pipe Parallel), BSPM, or BSP.
BSPF (British Standard Pipe Fitting) is the former term used for British Standard Parallel Threads. It was introduced to resolve confusion between BSPP (British Standard Pipe Parallel) and BSPT (British Standard Tapered Threads) regarding pronunciation.
The naming convention for British Standard Parallel Threads is as follows: G Size - Number of Threads per Inch, for example, G 1/8-28.
|
British Standard Parallel Threads BSPP=BSP=PF=G |
|||||
|
Size |
Threads per inch (TPI) |
Thread diameter (mm) |
Thread angle |
||
|
(inch) |
Major diameter |
Simple pitch diameter |
Minor diameter |
||
|
1/16 |
28 |
7.732 |
7.142 |
6.561 |
55° |
|
1/8 |
28 |
9.782 |
9.147 |
8.566 |
|
|
1/4 |
19 |
13.157 |
12.301 |
11.455 |
|
|
3/8 |
19 |
16.662 |
15.806 |
14.95 |
|
|
1/2 |
14 |
20.955 |
19.793 |
18.631 |
|
|
5/8 |
14 |
22.911 |
21.749 |
20.587 |
|
|
3/4 |
14 |
26.441 |
25.279 |
24.117 |
|
|
7/8 |
14 |
30.201 |
29.039 |
27.877 |
|
|
1 |
11 |
33.249 |
31.77 |
30.291 |
|
|
1-1/8 |
11 |
37.897 |
36.418 |
34.939 |
|
|
1-1/4 |
11 |
41.91 |
40.431 |
38.952 |
|
|
1-1/2 |
11 |
47.803 |
46.324 |
44.845 |
|
|
1-3/4 |
11 |
53.746 |
52.267 |
50.788 |
|
|
2 |
11 |
59.614 |
58.135 |
56.656 |
|
|
G Size-TPI |
|||||
British Standard Tapered Threads (BSPT=PT=R=RC=ZG):
British Standard Tapered Threads are commonly known as BSPT (The British Standard Pipe Taper), although the term "R Thread" has now replaced it. However, BSPT remains one of the widely accepted terms.
The naming convention for British Standard Tapered Threads is as follows: R Size - Number of Threads per Inch, for example, R 1/2-14.
|
British Standard Tapered Threads BSPT=PT=R=RC=ZG |
|||||
|
Size |
Threads per inch (TPI) |
Thread diameter (mm) |
Thread angle |
||
|
(inch) |
Major diameter |
Simple pitch diameter |
Minor diameter |
||
|
1/16 |
28 |
7.723 |
7.142 |
6.561 |
55° |
|
1/8 |
28 |
9.728 |
9.147 |
8.566 |
|
|
1/4 |
19 |
13.157 |
12.3 |
11.445 |
|
|
3/8 |
19 |
16.662 |
15.81 |
14.95 |
|
|
1/2 |
14 |
20.995 |
19.79 |
18.631 |
|
|
3/4 |
14 |
26.441 |
25.28 |
24.117 |
|
|
1 |
11 |
33.249 |
31.77 |
30.291 |
|
|
1-1/4 |
11 |
41.91 |
40.43 |
38.952 |
|
|
1-1/2 |
11 |
47.803 |
46.32 |
44.845 |
|
|
2 |
11 |
59.641 |
58.14 |
56.656 |
|
|
R Size-TPI |
|||||
ISO Metric Threads (M):
ISO Metric Threads are one of the first internationally recognized universal thread types. ISO 68-1 defines the design principles for metric threads. ISO Metric Threads consist of symmetrical V-shaped threads. The V-thread profile has a 60° thread angle, and both the external and internal threads are parallel.
ISO Metric Threads are denoted by the letter "M" (Metric) and come in two different pitch sizes: coarse and fine. Coarse threads are the most commonly used and have default pitch sizes; while fine threads have smaller pitch sizes. You can determine the thread size from the labeling format, such as "M4 * 0.5" — which indicates a thread diameter of 4 mm and a pitch size of 0.5 mm.
If the thread pitch corresponds to the commonly used coarse pitch listed in ISO 261 or ISO 262, it can be omitted (e.g., M8). For example, if only "M20" is given, it is a coarse thread.
The naming convention for metric straight threads is as follows: M Size - Pitch, for example, M 14 * 1.5.
|
ISO Metric Threads M |
|||||
|
Size |
Pitch |
Thread diameter (mm) |
Thread angle |
||
|
(inch) |
Major diameter |
Simple pitch diameter |
Minor diameter |
||
|
M6 |
1
|
6 |
5.35 |
4.917 |
60° |
|
M8 |
8 |
7.35 |
6.917 |
||
|
M10 |
10 |
9.35 |
8.917 |
||
|
M12 |
1.5
|
12 |
11.03 |
10.376 |
|
|
M14 |
14 |
13.03 |
12.376 |
||
|
M16 |
16 |
15.03 |
14.376 |
||
|
M18 |
18 |
17.03 |
16.376 |
||
|
M20 |
20 |
19.03 |
18.376 |
||
|
M22 |
22 |
21.03 |
20.376 |
||
|
M24 |
24 |
23.03 |
22.376 |
||
|
M27 |
2
|
27 |
25.7 |
24.835 |
|
|
M30 |
30 |
28.7 |
27.835 |
||
|
M33 |
33 |
31.7 |
30.835 |
||
|
M36 |
36 |
34.7 |
33.835 |
||
|
M Size x Pitch |
|||||
(5) Four Steps to Identify Thread Specifications
|
Thread Standard |
Step 1 |
Step 2 |
Step 3 |
Step 4 |
|
Determine the Type of Thread |
Determine the Pitch of Thread |
Determine the Size of Thread |
Determine the Thread Standard |
|
|
American Standard Straight Threads (SAE=UN=UNF) |
Straight |
12、14、16 18、20、24 |
Measuring using: Vernier caliper Dial caliper Digital caliper |
Size-TPI, Type e.g. 3/4-16, UN |
|
American Standard Tapered Threads (NPT / NPTF) |
Tapered |
11-1/2、14 18、27 |
Size-TPI, Type |
|
|
British Standard Parallel Threads (BSPP=BSP=PF=G) |
Straight |
11、14 19、28 |
G Size-TPI |
|
|
British Standard Tapered Threads (BSPT=PT=R=RC=ZG) |
Tapered |
11、14 19、28 |
R Size-TPI |
|
|
ISO Metric Threads M |
Straight |
1.0、1.5、2.0 |
M Size x Pitch |
Now that you've learned how to select the thread type and size, are you wondering how to install the instrument? Click the link below to learn about the installation process and related precautions!
- Top Six Common Reasons of Pressure Equipment Failure
- Key Safety Points for Installing Pressure Gauges
- ASME: Pipe Threads, General Purpose, Inch
- ISO 68-1:1998(en) ISO general purpose screw threads — Basic profile — Part 1: Metric screw threads
- ISO/DIS 6149-1(en) Connections for hydraulic fluid power and general use — Ports and stud ends with ISO 261 metric threads and O-ring sealing — Part 1: Ports with truncated housing for O-ring seal
- ISO 262:1998 ISO general purpose metric screw threads — Selected sizes for screws, bolts and nuts








